Dangers And Treatment Methods Of Varicose Veins Essay
Dangers And Treatment Methods Of Varicose Veins Essay
Varicose veins are a typical condition portrayed by purple or pale blue swelling veins. The condition is most usually created in the legs and feet however can create on any piece of the body. Varicose veins happen frequently in the lower limits because of the expanded weight of standing and strolling. This condition is experienced by up to 25 for every penny of American grown-ups sooner or later in their lives. Varicose veins and arachnid veins are unwanted for the most part because of their appearance. Numerous individuals experiencing this condition build up an unsure propensity for endeavoring to cover or camouflage the veins. Be that as it may, this isn’t just a restorative issue. For a few people, the veins cause agony and throbbing and can cause significant issues whenever left untreated. Now and again, varicose veins can show an expanded danger of circulatory issue. The most well-known beginning treatments for varicose veins incorporate various self improvement strategies. Dangers And Treatment Methods Of Varicose Veins Essay.
ORDER A PLAGIARISM -FREE PAPER NOW
These incorporate way of life adjustments, dietary changes and the utilization of pressure tights. Extra treatments are accessible relying on the seriousness and discomfort of the condition. Most modern systems are negligibly obtrusive and don’t require a protracted doctor’s facility remain or recuperation period. Before choosing a careful treatment, talk about different choices with your doctor. Exercise, weight reduction, hoisting the legs, wearing pressure leggings, and abstaining from sitting or remaining for significant lots of time can help keep the condition or moderate its encouraging. In the event that these strategies don’t cause a change, the doctor may prescribe more specific treatments. A standout amongst the most encouraging treatments for varicose veins is the VNUS Closure technique. This is a negligibly obtrusive treatment that outcomes in less wounding and less torment than a few of the more conventional alternatives. This strategy is performed by embeddings a catheter into the influenced vein and applying heat, causing the collagen in the vein divider to therapist and close the vein. The blood will re-course to other solid veins when the influenced vein is fixed. With the Closure treatment, the system is performed through a little cut in the lower leg. Dangers And Treatment Methods Of Varicose Veins Essay. This wipes out the requirement for more confounded medical procedure requiring general anesthesia. The system is normally performed under nearby anesthesia in a specialist’s office. Since this treatment does not require evacuating the dangerous vein or other excruciating methods, it results in less agony and wounding and in addition a considerably faster recuperation period. This strategy enables patients to come back to their typical day by day schedule in a significantly shorter timeframe than with different techniques.
The VNUS Closure method brags a 97 for each penny adequacy rate, which implies it is extremely compelling and being delicate on the patient. It likewise results in insignificant to no scarring, making it more cosmetically engaging than treatments requiring obtrusive careful strategies. This treatment, and additionally other varicose vein strategies, is for the most part exceptionally compelling. It is essential to recollect, notwithstanding, that not all treatments are appropriate for each patient. Examine your alternatives with your doctor before settling on any choice about treating your varicose veins. A wandering phlebectomy is another case of a more seasoned treatment strategy, yet a few patients still incline toward this technique. With this technique, a doctor hauls out the vessel with an uncommon apparatus. Once evacuated, different vessels assume control quickly. The advantage of a mobile phlebectomy is quick outcomes without sitting tight for reabsorption. Dangers And Treatment Methods Of Varicose Veins Essay.
Fresher Options
Today specialists use fresher, further developed strategies to reestablish vascular wellbeing. One system includes embeddings a thin catheter into the defective vein. By applying radio waves, the vessel divider therapists and breakdown. Patients don’t encounter scarring after this method, however a few people will see wounding. The last reabsorption may take up to two months to finish. Laser treatment is a well known and non-obtrusive varicose veins treatment. A specialist guides a laser to force the vessel to fall. Patients may encounter slight discomfort when the laser pillar hits the skin. Restorative work force instantly decrease this discomfort by cooling the skin. Froth sclerotherapy includes blending a unique cleanser with air to make a prescription that takes after thin shaving cream. The specialist infuses the froth, causing swelling and blockage. When this happens, different venous frameworks venture up to deal with the blood stream. This kind of treatment is best for less serious issues.
Varicose veins are large, swollen veins that often appear on the legs and feet. They happen when the valves in the veins do not work properly, so the blood does not flow effectively.
The veins rarely need treatment for health reasons, but if swelling, aching, and painful legs result, and if there is considerable discomfort, treatment is available.
There are various options, including some home remedies.
In severe cases, a varicose vein may rupture, or develop into varicose ulcers on the skin. These will require treatment.
If the patient has no symptoms or discomfort and is not bothered by the sight of the varicose veins, treatment might not be necessary. However, if there are symptoms, treatment may be required to reduce pain or discomfort, address complications, such as leg ulcers, skin discoloration, or swelling.
Some patients may also want treatment for cosmetic reasons – they want to get rid of the “ugly” varicose veins.
Surgery
If varicose veins are large, they may need to be removed surgically. This is usually done under general anesthetic. In most cases, the patient can go home the same day – if surgery is required on both legs, they may need to spend one night in hospital.
Laser treatments are often used to close off smaller veins, and also spider veins. Strong bursts of light are applied to the vein, which gradually fades and disappears.
Ligation and stripping
Two incisions are made, one near the patient’s groin at the top of the target vein, and the other is made further down the leg, either at the ankle or knee. The top of the vein is tied up and sealed. A thin, flexible wire is threaded through the bottom of the vein and then pulled out, taking the vein with it.
This procedure does not usually require a hospital stay. Ligation and stripping can sometimes result in bruising, bleeding, and pain. In extremely rare occasions, there may be deep vein thrombosis.
After surgery, most patients will need 1-3 weeks to recover before going back to work and other normal duties. During recovery time, compression stockings are worn.
Sclerotherapy
A chemical is injected into small and medium-sized varicose veins, which scars and closes them. A few weeks later, they should fade. A vein may need to be injected more than once.
Radiofrequency ablation
A small incision is made either above or below the knee, and with the help of an ultrasound scan; a narrow tube (catheter) is threaded into the vein.
The doctor inserts a probe into the catheter, which emits radiofrequency energy. The radiofrequency energy heats up the vein, causing its walls to collapse, effectively closing it and sealing it shut. This procedure is preferred for larger varicose veins. Radiofrequency ablation is usually done with a local anesthetic.
Endovenous laser treatment
A catheter is inserted into the patient’s vein. A small laser is threaded through the catheter and positioned at the top of the target vein; it delivers short energy bursts that heat up the vein, sealing it shut.
With the aid of an ultrasound scan, the doctor threads the laser all the way up the vein, gradually burning and sealing all of it. This procedure is done under local anesthetic. There may be some nerve injury, which is usually brief. Dangers And Treatment Methods Of Varicose Veins Essay.
Transilluminated powered phlebectomy
An endoscopic transilluminator (special light) is threaded through an incision under the skin so that the doctor can see which veins need to be taken out. The target veins are cut and removed with a suction device through the incision.
A general or local anesthetic may be used for this procedure. There may be some bleeding and bruising after the operation.
In the majority of cases, there is no pain, but signs and symptoms of varicose veins may include:
- veins look twisted, swollen, and lumpy (bulging)
- the veins are blue or dark purple
Some patients may also experience:
- aching legs
- legs feel heavy, especially after exercise or at night
- a minor injury to the affected area may result in longer bleeding than normal
- lipodermatosclerosis – fat under the skin just above the ankle can become hard, resulting in the skin shrinking
- swollen ankles
- telangiectasia in the affected leg (spider veins)
- there may be a shiny skin discoloration near the varicose veins, usually brownish or blue in color
- venous eczema (stasis dermatitis) – skin in the affected area is red, dry, and itchy
- when suddenly standing up, some individuals experience leg cramps
- a high percentage of people with varicose veins also have restless legs syndrome
- atrophie blanche – irregular whitish patches that look like scars appear at the ankles
Complications
Any condition in which proper blood flow is undermined has a risk of complications. However, in the majority of cases, varicose veins have no complications. If complications do occur, they may include:
- Bleeding.
- Thrombophlebitis: Blood clots in the vein of the leg cause inflammation of the vein.
- Chronic venous insufficiency – the skin does not exchange oxygen, nutrients, and waste products with the blood properly because the blood flow is weak. Dangers And Treatment Methods Of Varicose Veins Essay. Chronic venous insufficiency is not caused by varicose veins, but the two entities are closely related.
People with chronic venous insufficiency may develop varicose eczema, lipodermatosclerosis (hard and tight skin), and venous ulcers. Venous ulcers classically form around ankles and are often preceded by a discolored area. It is important to get medical evaluation for chronic venous insufficiency.
The veins have one-way valves so that the blood can travel in only one direction. If the walls of the vein become stretched and less flexible (elastic), the valves may get weaker. A weakened valve can allow blood to leak backward and eventually flow in the opposite direction. When this occurs, blood can accumulate in the vein(s), which then become enlarged and swollen.
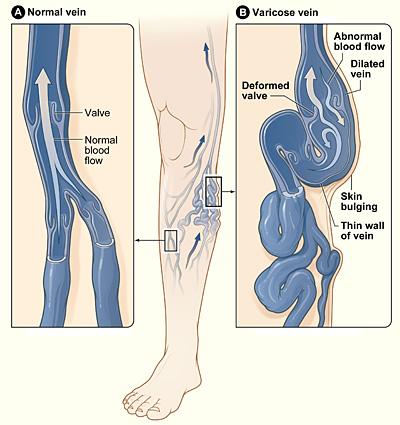
Figure A shows a normal vein with a properly working valve. In Figure B, the varicose vein has a faulty valve, the walls of the vein are thin and stretched.
Image credit: National Heart Lung and Blood Institute.
The veins furthest from the heart are most often affected, such as those in the legs. This is because gravity makes it harder for blood to flow back to the heart. Any condition that puts pressure on the abdomen has the potential to cause varicose veins; for instance, pregnancy, constipationand, in rare cases, tumors.
Risk factors
Experts are not sure why the walls of veins stretch or why the valves become faulty. In many cases, it occurs for no clear reason. However, some potential risk factors include:
- menopause
- pregnancy
- being aged over 50
- standing for long periods
- family history of varicose veins
- obesity
The following risk factors are linked to a higher risk of having varicose veins:
- Gender: Varicose veins affect women more often than males. It may be that female hormones relax veins. If so, taking birth control pills or hormone therapy (HT) might contribute.
- Genetics: Varicose veins often run in families.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese increases the risk of varicose veins.
- Age: The risk increases with age, due to wear and tear on vein valves.
- Some jobs: An individual who has to spend a long time standing at work may have a higher chance of varicose veins. Dangers And Treatment Methods Of Varicose Veins Essay.
Pregnancy and varicose veins
Women are much more likely to develop varicose veins during their pregnancy than at any other time in their lives. Pregnant women have much more blood in their body; this places extra pressure on the circulatory system.
Additionally, changes in hormone levels can lead to a relaxation of the blood vessel walls. Both these factors raise the risk of having varicose veins.
As the uterus (womb) grows, there is more pressure on the veins in the mother’s pelvic area. In the majority of cases, the varicose veins go away after the pregnancy is over; this is not always the case, and sometimes, even if the varicose veins improve, there may be some left visible.
Varicose veins are tortuous, widened veins in the subcutaneous tissues of the legs and are often easily visible. Their valves are usually incompetent so that reflux of blood occurs, and the resulting venous hypertension can cause symptoms. Varicose veins are widely seen as medically unimportant and deserving low priority for treatment. They are common, affecting nearly a third of adults in Western societies, and few people with varicose veins are ever harmed by them. However, they cause concern and distress on a large scale, most of which can be dealt with by good explanation and reassurance, or by a variety of treatments which are evolving rapidly at present. Patients can now be referred for more precise assessment and a greater range of therapeutic options than ever before.
Who gets varicose veins?
A large UK population study has shown age adjusted prevalences of 40% in men and 32% in women, although women more often present for treatment.1 The age of onset varies; some people develop varicose veins in their teens, but prevalence rises with age. Varicose veins often appear first in pregnancy, and further pregnancies can make them worse. A family history is common,1 but people should be reassured that having close relatives with severe symptoms from varicose veins or ulcers does not confer any great likelihood that they will have similar problems. Dangers And Treatment Methods Of Varicose Veins Essay.
What problems can varicose veins cause?
Cosmetic concern
For the great majority of people varicose veins cause no symptoms and never cause harm. Dislike of their appearance is a common complaint, particularly for women. Cosmetic concern may increase the emphasis that patients place on other symptoms.
Fears about future harm
A questionnaire study found that many people are worried about the possible harm their varicose veins might cause, but these fears are usually inappropriate—particularly in relation to bleeding, ulcers, and deep vein thrombosis.2
Discomfort
Varicose veins can cause a variety of symptoms of discomfort in the legs, but it is important to try to differentiate these from the many other reasons for leg pains. The Edinburgh vein study found that the symptoms significantly associated with varicose vein were itching, heaviness, and aching, but the relation of these with varicose veins was inconsistent, particularly in men.3 Traditional pointers to symptoms being caused by varicose veins include worsening of symptoms after prolonged standing or walking and towards the end of the day, relieving symptoms by elevating the legs or wearing support hosiery, and tenderness over the veins. Dangers And Treatment Methods Of Varicose Veins Essay.
Leg swelling
This is an uncommon symptom of varicose veins—other causes are much commoner. Unilateral swelling of a leg with big varicose veins is the most typical presentation.
Thrombophlebitis
Superficial thrombophlebitis (“phlebitis”) can complicate varicose veins. The risk of deep vein thrombosis is remote, but in a case series it occurred very occasionally if phlebitis extended above the knee.4 Veins may sometimes remain permanently occluded. Treatment of the varicose veins may be appropriate if phlebitis is recurrent or severe, or if the veins also cause other symptoms. Note that thrombophlebitis is not caused by infection, and treatment with antibiotics is unnecessary: drug treatment should be limited to anti-inflammatory analgesics.
Bleeding, skin changes, and ulcers
These are the complications of varicose veins that mandate consideration of treatment. They are all associated with high venous pressure in the upright position, as a result of incompetent venous valves. Bleeding is uncommon and usually occurs from a prominent vein on the leg or foot with thin, dark, unhealthy skin overlying it. “Skin changes” range from eczema, through brown discoloration, to florid lipodermatosclerosis with induration of the subcutaneous tissues (fig 1). Sometimes this can become painfully inflamed—“inflammatory liposclerosis”—which is often misdiagnosed as phlebitis or infection. If neglected, lipodermatosclerosis can lead to ulceration, which can be chronic and troublesome: treatment of ulcers will not be considered in this review.

Skin changes (lipodermatosclerosis) caused by venous hypertension. Recognition of skin damage is fundamental in examination of varicose veins
What other conditions can varicose veins be confused with?
Many people have telangiectases on their legs—often called thread, spider, or broken veins. Small dark blue reticular veins are also common. All of these are of cosmetic importance only. They are not the same as varicose veins, though they often occur in association with them.
Many people with varicose veins worry about deep vein thrombosis, but the superficial veins of the legs that become varicose are separate and distinct from the deep veins where deep vein thrombosis occurs. Varicose veins pose no proved risk of deep vein thrombosis during people’s normal daily lives. Varicose veins occurring as a result of a deep vein thrombosis are uncommon. However, varicose veins may coexist with deep vein incompetence, particularly in people with complications such as lipodermatosclerosis or ulcers, which makes treatment more difficult.
How should varicose veins be assessed?
Examination should be done with the patient standing in good light, when the extent and size of varicose veins and the presence of other venous blemishes (such as telangiectases) will be clear. The distribution of varicose veins may well suggest that they are related to the long or short saphenous system. Sometimes a large varix with a palpable defect in the fascia beneath provides clinical evidence of an incompetent perforating vein. The most important medical issue is the presence or absence of skin damage resulting from venous hypertension.
Tourniquet tests (such as the Trendelenberg test) have been abandoned by vascular specialists: they are inaccurate and have been superseded by the use of ultrasonography. Knowledge of the principle of tourniquet tests seems to persist in professional examinations as a test of the understanding of venous incompetence and the usual sites where it occurs. Incompetence at the saphenofemoral junction in the groin is by far the commonest: less common sites are the saphenopopliteal junction behind the knee, various perforating veins, and the deep veins . Dangers And Treatment Methods Of Varicose Veins Essay.
